The SR periodic table is an essential reference tool in chemistry, particularly for understanding the properties and behaviors of elements like strontium. Strontium, represented by the symbol Sr, is a fascinating element with various applications in science and industry. This article will explore the characteristics of strontium, its position in the periodic table, and its significance in different fields, including medicine, industry, and environmental science.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the physical and chemical properties of strontium, its isotopes, and its role in everyday life. Understanding the SR periodic table is crucial for students, educators, and professionals in scientific fields. Whether you are a chemistry enthusiast or a student preparing for an exam, this article aims to provide valuable insights into strontium and its applications.
By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of strontium's significance in the SR periodic table and its practical implications. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of strontium and explore what makes it a unique and important element.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Strontium
- 2. Physical Properties of Strontium
- 3. Chemical Properties of Strontium
- 4. Isotopes of Strontium
- 5. Applications of Strontium
- 6. Environmental Impact of Strontium
- 7. Health Effects of Strontium
- 8. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Strontium
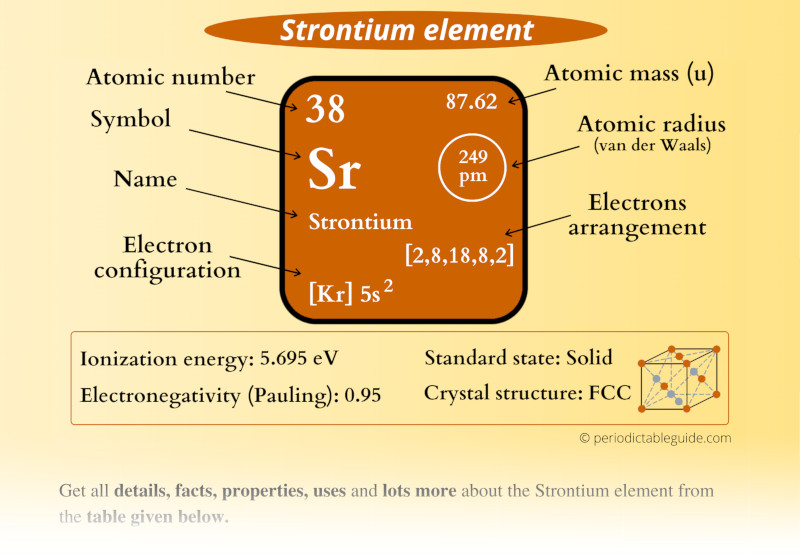
Strontium is an alkaline earth metal that belongs to Group 2 of the periodic table. It was discovered in 1790 by the chemist William Cruickshank in the mineral strontianite. Strontium is known for its silvery-white metallic appearance and is highly reactive, especially in the presence of air and moisture. It is primarily obtained through the extraction of minerals such as celestine and strontianite.
As the 38th element in the periodic table, strontium has an atomic number of 38 and an atomic weight of approximately 87.62 g/mol. It is often used in fireworks and flares due to its ability to produce a bright red flame when burned. Strontium also has several important applications in various fields, which will be discussed in detail later in this article.
2. Physical Properties of Strontium
The physical properties of strontium are essential for understanding its behavior and applications. Here are some key characteristics:
- Appearance: Strontium is a soft, silvery-white metal.
- Density: The density of strontium is approximately 2.64 g/cm³.
- Melting Point: Strontium has a melting point of around 777 °C (1,451 °F).
- Boiling Point: The boiling point of strontium is approximately 1,382 °C (2,520 °F).
- Reactivity: Strontium reacts vigorously with water and forms strontium hydroxide.
3. Chemical Properties of Strontium
Strontium exhibits several notable chemical properties that are important for its reactions and compounds:
- Oxidation States: The most common oxidation state of strontium is +2.
- Compounds: Strontium forms various compounds, including strontium oxide (SrO) and strontium carbonate (SrCO₃).
- Reaction with Halogens: Strontium reacts with halogens to form strontium halides, such as strontium chloride (SrCl₂).
- Flame Color: Strontium compounds produce a characteristic red color when burned, making them popular in pyrotechnics.
4. Isotopes of Strontium
Strontium has several isotopes, with strontium-88 being the most abundant. Here is a brief overview of the isotopes:
- Strontium-84: Stable isotope, 0.56% abundance.
- Strontium-86: Stable isotope, 9.86% abundance.
- Strontium-87: Radioactive isotope, commonly used in radiometric dating.
- Strontium-88: Most abundant and stable isotope, approximately 82.58% abundance.
5. Applications of Strontium
Strontium has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Medicine: Strontium ranelate is used in the treatment of osteoporosis.
- Pyrotechnics: Strontium compounds are used in fireworks to produce red flames.
- Electronics: Strontium is used in the production of cathode ray tubes.
- Glass Manufacturing: Strontium is added to glass formulations to improve strength and clarity.
6. Environmental Impact of Strontium
As with many elements, the environmental impact of strontium is a consideration, particularly in areas where it is mined or used industrially. Strontium can enter the environment through various pathways, including:
- Mining Activities: Mining of strontium-containing minerals can lead to habitat destruction and pollution.
- Radioactive Isotopes: Strontium-90, a byproduct of nuclear fission, poses environmental and health risks.
- Water Contamination: Strontium can leach into water sources, affecting drinking water quality.
7. Health Effects of Strontium
Strontium can have both beneficial and harmful effects on health, depending on its form and concentration:
- Beneficial Effects: Strontium ranelate can help strengthen bones in osteoporosis patients.
- Harmful Effects: Exposure to high levels of radioactive strontium can lead to health issues, including cancer.
- Regulatory Standards: Various health agencies monitor and regulate strontium exposure levels to protect public health.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the SR periodic table provides valuable information about strontium, an element with diverse applications and significant properties. Understanding the characteristics of strontium is essential for students, educators, and professionals in various fields. From its physical and chemical properties to its applications in medicine and industry, strontium plays a crucial role in modern science.
We encourage you to leave a comment below, share this article with others, or explore more articles on our site to deepen your understanding of chemistry and the periodic table.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you again on our site!