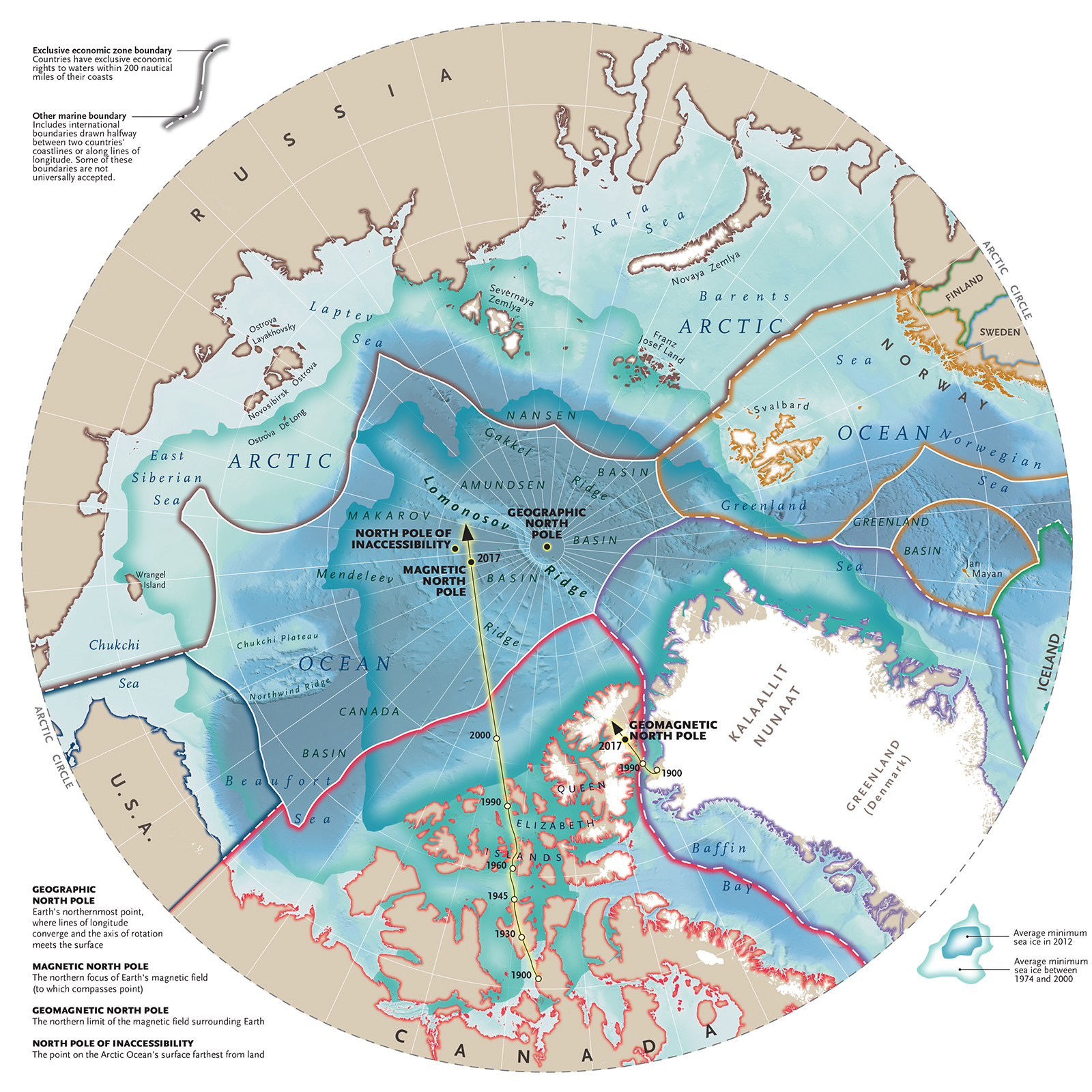
The North Pole, a region steeped in mystery and allure, has fascinated explorers, scientists, and adventurers for centuries. Understanding the map of the North Pole is not just about geography; it's about exploring the unique natural phenomena, climatic conditions, and the rich history of human exploration in one of the most inhospitable places on Earth. In this article, we will delve deep into the various aspects of the North Pole, including its geographical significance, historical explorations, environmental challenges, and much more. Through this comprehensive guide, readers will gain valuable insights into the North Pole's map, its features, and why it continues to be a point of interest in global discussions about climate change and international politics.
The North Pole is often depicted as the ultimate frontier, a place where the Earth's axis meets the Arctic Ocean. Its geographical coordinates are 90°N latitude, with no defined longitude since all lines of longitude converge at this point. However, the area surrounding the North Pole is rich in unique geographical features such as sea ice, icebergs, and the Arctic Ocean, which all contribute to the North Pole's fascinating ecosystem. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of the map of the North Pole, highlighting its importance and the various factors that influence this extreme environment.
In addition to geographical elements, the North Pole plays a crucial role in global weather patterns and climate systems. The map of the North Pole serves not only as a navigational tool but also as a vital resource for scientific research and environmental monitoring. As we navigate through this article, we will explore the historical context, the current geopolitical landscape, and the environmental challenges that the North Pole faces today.
Table of Contents
- Geographical Significance of the North Pole
- Historical Exploration of the North Pole
- Environmental Challenges Facing the North Pole
- Scientific Research at the North Pole
- Geopolitical Issues Surrounding the North Pole
- Understanding the Map of the North Pole
- The Future of the North Pole
- Conclusion
Geographical Significance of the North Pole
The North Pole is located at the northernmost point of the Earth, where all lines of longitude converge. Its geographical significance can be understood through the following aspects:
- Climate: The North Pole experiences extreme weather conditions characterized by long, harsh winters and brief, cool summers.
- Oceanography: The Arctic Ocean, which surrounds the North Pole, plays a crucial role in the Earth's climate system.
- Flora and Fauna: The North Pole is home to unique species adapted to extreme cold, including polar bears, seals, and various migratory birds.
The Arctic Ocean and Its Role
The Arctic Ocean is integral to understanding the map of the North Pole. It acts as a barrier, influencing the climate and ecological dynamics of the region. The ocean is covered by sea ice, which varies in thickness and extent throughout the year. This ice cover is essential for the survival of various Arctic species and serves as a critical indicator of climate change.
Historical Exploration of the North Pole
The quest to reach the North Pole has a rich and storied history, marked by daring expeditions and remarkable achievements:
- First Attempts: Early explorers such as John Franklin and Sir Edward Parry made significant contributions to Arctic exploration in the 19th century.
- Successful Reaches: In 1909, Robert Peary claimed to have reached the North Pole, a claim that has been the subject of considerable debate.
- Modern Expeditions: Today, advancements in technology have allowed for more precise exploration and mapping of the North Pole.
Impact of Exploration on the North Pole
Exploration has had lasting impacts on the North Pole, including environmental changes and geopolitical implications. As human activity increases in the region, understanding its historical context becomes crucial.
Environmental Challenges Facing the North Pole
The North Pole faces numerous environmental challenges primarily driven by climate change. Some of the most pressing issues include:
- Melting Ice Caps: The rate of ice melt in the Arctic is accelerating, threatening habitats and global sea levels.
- Pollution: Increased shipping traffic and industrial activities contribute to pollution in the Arctic region.
- Wildlife Threats: The changing environment poses significant risks to native species and their habitats.
Climate Change and Its Impacts
Climate change is arguably the most significant threat to the North Pole. The region is warming at a rate twice as fast as the global average, leading to profound changes in its ecosystem.
Scientific Research at the North Pole
Scientific research in the North Pole is vital for understanding global climate change and its implications. Key areas of focus include:
- Climate Monitoring: Scientists use the North Pole as a critical point for monitoring climate patterns and changes.
- Ecological Studies: Research on Arctic wildlife helps in understanding the impacts of climate change on biodiversity.
- Geopolitical Research: The North Pole's strategic importance has led to increased research on international relations and territorial claims.
Collaborative Research Efforts
International collaboration is crucial for effective scientific research in the North Pole. Various countries and organizations work together to address the challenges posed by climate change and to promote sustainable practices.
Geopolitical Issues Surrounding the North Pole
The North Pole is not only a geographical point but also a center of geopolitical interest. Key issues include:
- Territorial Claims: Countries surrounding the Arctic seek to assert their claims over the region's resources.
- Shipping Routes: Melting ice is opening new shipping routes, raising questions about navigation rights and environmental protection.
- International Treaties: Agreements such as the Arctic Council play a crucial role in managing international relations in the Arctic.
Impact of Geopolitics on Environmental Policies
Geopolitical interests often clash with environmental conservation efforts, leading to complex challenges in governance and policy-making in the Arctic region.
Understanding the Map of the North Pole
The map of the North Pole is a unique representation of one of the Earth's most extreme environments. Key elements to consider include:
- Geographical Features: Understanding the layout of sea ice, icebergs, and surrounding landmasses is essential.
- Climate Zones: The map illustrates the various climate zones, which are vital for ecological studies.
- Navigation: Modern maps are crucial for navigation and research expeditions in the Arctic region.
Modern Mapping Technologies
Advancements in mapping technologies, such as satellite imagery and GIS, have significantly improved our understanding of the North Pole. These tools allow for real-time monitoring of environmental changes and contribute to more accurate data collection.
The Future of the North Pole
The future of the North Pole remains uncertain, but several trends indicate significant changes ahead. These include:
- Continued Climate Change: Unless addressed, climate change will lead to further ice melt and ecological disruption.
- Increased Human Activity: Exploration and commercial interests in the region may lead to environmental degradation.
- International Cooperation: The need for effective governance and international agreements is more crucial than ever.
Call for Sustainable Practices
To protect the North Pole's unique environment, there is an urgent need for sustainable practices that balance exploration and conservation efforts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the map of the North Pole is not just a geographical representation; it embodies the complexities of climate change, geopolitical interests, and scientific exploration. As we continue to navigate the challenges facing this unique region, it is crucial to foster international cooperation and sustainable practices to ensure its preservation for future generations. We invite readers to share their thoughts in the comments section, explore related articles, and stay informed about this fascinating topic.
Thank you for reading! We hope you found this article informative and engaging. Please visit our site again for more insightful content on geography, science, and environmental issues.