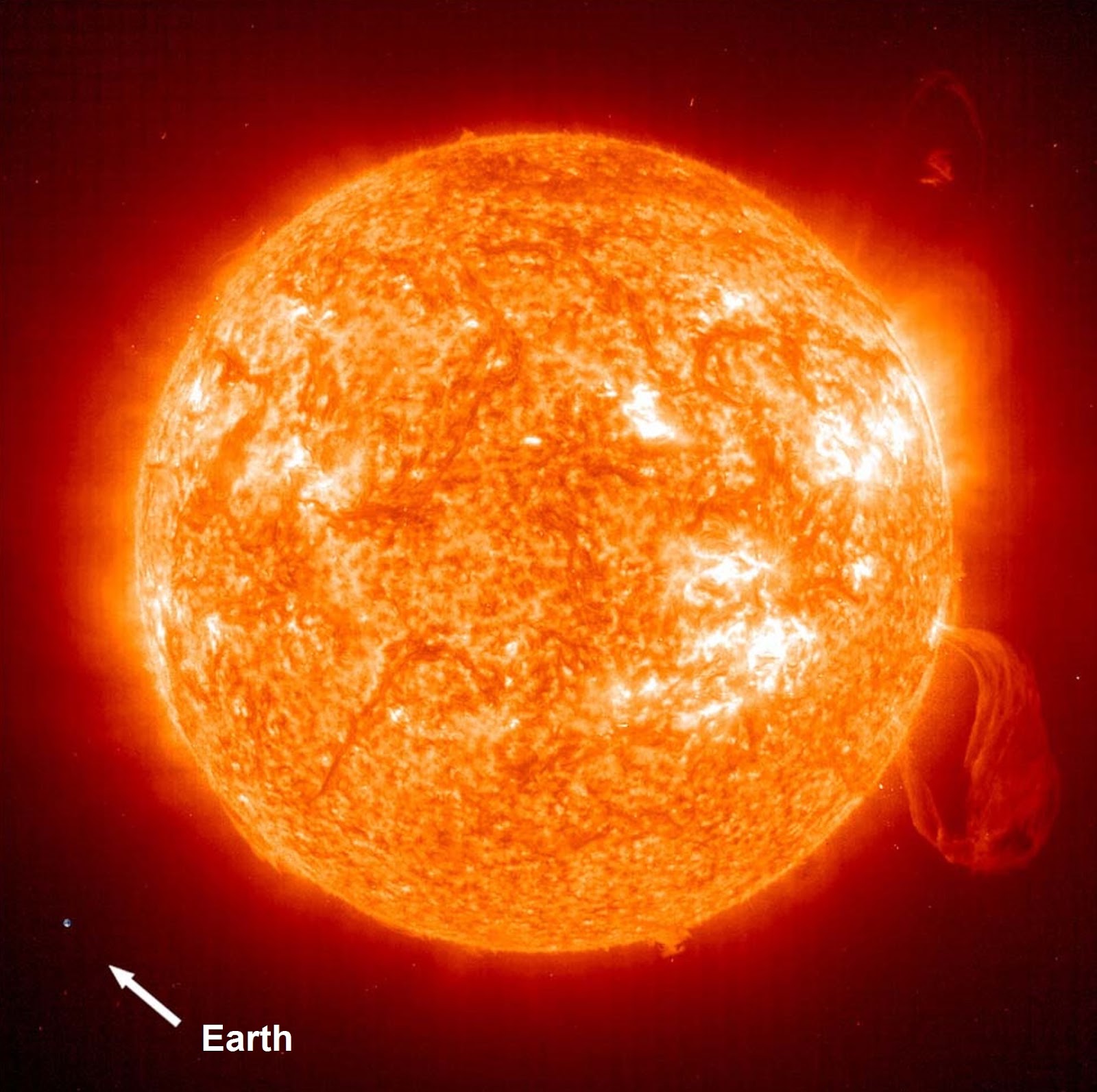
When we think about our planet, Earth, we often wonder how it compares to the Sun, the giant star that sustains life on our planet. Understanding the differences and similarities between Earth and the Sun not only satisfies our curiosity but also enhances our knowledge of the universe. In this article, we will explore various aspects of both celestial bodies, including their size, composition, temperature, and role in the solar system.
Earth, the third planet from the Sun, is a unique and dynamic world, characterized by its diverse ecosystems and life forms. In contrast, the Sun is a massive ball of gas at the center of our solar system, providing the energy necessary for life on Earth. This article will delve into the fascinating comparison between Earth and the Sun, shedding light on their fundamental characteristics and interrelationship.
By the end of this article, readers will have a clearer understanding of how Earth compares to the Sun in various dimensions, including physical attributes, scientific significance, and their roles in the cosmos. Let's embark on this enlightening journey and uncover the mysteries of our planet and its stellar companion.
Table of Contents
- 1. Basic Characteristics of Earth and Sun
- 2. Size Comparison: Earth vs. Sun
- 3. Composition and Structure of Earth and Sun
- 4. Temperature Differences: Earth and Sun
- 5. The Role of Earth in the Solar System
- 6. The Sun's Influence on Earth
- 7. Scientific Observations and Discoveries
- 8. Conclusion and Future Exploration
1. Basic Characteristics of Earth and Sun
Earth is a terrestrial planet that supports a variety of life forms, while the Sun is a star composed primarily of hydrogen and helium. Below are some basic characteristics of each:
- Earth: Diameter: 12,742 km, Atmosphere: Nitrogen and Oxygen, Surface: 71% water.
- Sun: Diameter: 1,391,000 km, Composition: 74% Hydrogen, 24% Helium, Surface Temperature: 5,500°C.
2. Size Comparison: Earth vs. Sun
One of the most striking differences between Earth and the Sun is their size. The Sun is approximately 109 times wider than Earth and contains about 99.86% of the total mass of the solar system. To put this into perspective:
- The volume of the Sun could fit approximately 1.3 million Earths inside it.
- Earth's diameter is about 12,742 km, while the Sun's diameter is about 1,391,000 km.
Why Size Matters
The sheer size of the Sun plays a crucial role in its gravitational influence on Earth and other celestial bodies, enabling the formation of orbits and maintaining stability within the solar system.
3. Composition and Structure of Earth and Sun
Earth is composed of a solid crust, a viscous mantle, and a molten outer core surrounding a solid inner core. In contrast, the Sun is primarily composed of gases, with a core that undergoes nuclear fusion, producing energy that radiates outward.
Earth's Composition
- Crust: The outermost layer where we live.
- Mantle: The thick layer of rock beneath the crust.
- Core: Composed of iron and nickel, divided into outer and inner cores.
Sun's Composition
- Core: About 15 million °C, where nuclear fusion occurs.
- Radiative Zone: Energy moves outward through radiation.
- Convective Zone: Hot plasma rises and cooler plasma sinks.
4. Temperature Differences: Earth and Sun
The temperature of the Sun is significantly higher than that of Earth. While the average surface temperature of Earth is about 15°C, the Sun's surface temperature reaches around 5,500°C. In the core, temperatures soar to about 15 million °C.
Impact of Temperature on Life
The moderate temperatures on Earth are essential for sustaining life. The Sun's high temperatures allow for the process of nuclear fusion, which produces the energy that reaches Earth, making life possible.
5. The Role of Earth in the Solar System
Earth is the only known planet to support life, and its unique position in the solar system is critical for maintaining conditions suitable for life. It orbits the Sun at an average distance of about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers), a distance known as an astronomical unit (AU).
Earth's Unique Features
- Water: Covers 71% of the Earth's surface.
- Atmosphere: Protects life from harmful solar radiation.
- Biodiversity: Home to millions of species across various ecosystems.
6. The Sun's Influence on Earth
The Sun exerts a powerful influence on Earth, affecting climate, weather patterns, and the seasons. Solar energy drives photosynthesis, which is the foundation of the food chain.
Solar Activity's Effects
- Solar Flares: Sudden eruptions of energy that can disrupt communication systems.
- Solar Winds: Streams of charged particles that interact with Earth's magnetosphere.
7. Scientific Observations and Discoveries
Throughout history, scientists have made significant discoveries about both Earth and the Sun, enhancing our understanding of their characteristics and interactions. Instruments such as telescopes and satellites have provided valuable data.
Key Discoveries
- Understanding solar activity and its impact on Earth.
- Satellite missions like SOHO (Solar and Heliospheric Observatory) have provided insight into solar dynamics.
8. Conclusion and Future Exploration
In conclusion, the comparison between Earth and the Sun reveals fundamental differences and interdependencies that sustain life on our planet. As we continue to explore our solar system, further discoveries will enhance our understanding of these celestial bodies.
We invite readers to share their thoughts on this article and explore more about the universe. Leave a comment below, and don't forget to check out our other articles for more fascinating insights!
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of Earth compared to the Sun. We look forward to seeing you again for more informative content.